
Rain and snow that falls directly on rivers and streams becomes one part of stream flow. Precipitation that falls directly onto the oceans becomes part of Surface Ocean and can be churned by wave and wind action into ocean currents. Fog and mist, falling water in gas or vapor form. Snow, ice, hail, and sleet are falling water in solid or frozen form. PRESENTER: Rain is falling water in liquid form. You could have precipitation in many forms- rain, snow, hail. ANNA MICHALAK: Precipitation is the process of water falling onto the surface of the Earth.

And there is a name for every kind of movement in the water cycle, starting with precipitation. Water in all its forms is always in flux and always moving. And beneath the soil, in water tables and underground aquifers like the Ogallala-High Plains, which runs underneath parts of eight states, from South Dakota to Texas. In and on plants and trees rooted in the soil. In the snow packs atop mountains like the Sierra Nevada. In the ice sheets and glaciers, 2/3 of all the freshwater on Earth. PRESENTER: There's a lot of water in the ocean- 70% of all the water on Earth. Either way, there's water- sometimes, a little. TOM HARMON: There's always a little bit of water in the atmosphere.
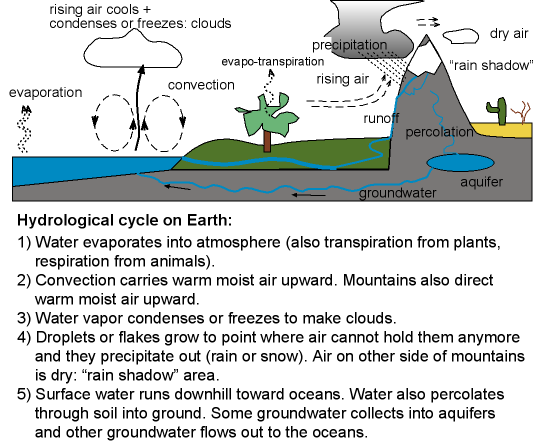
Summarize the steps of the water cycle. series#
The water cycle is a series of flows of water between various water stores, or storages- clouds in the atmosphere.
Summarize the steps of the water cycle. how to#
PRESENTER: How to summarize what is known about the water cycle? With two words- flows and stores. It's something that's around us all the time. MARTHA CONKLIN: The water cycle is fascinating. Yet, so complex, the most advanced Earth scientists- hydrologists, geologists, and biogeochemists- are studying every part and process. PRESENTER: The water cycle, so simple even small children understand the basics. ANNA MICHALAK: Why is there life on Earth? And the reason there is life on Earth is because Earth has this perfect water cycle. Eventually, evaporating into the air and condensing into clouds, again. Falling as rain and snow from clouds to the Earth's surface. The same water flowing in a continuous loop. Fresh water is actually, millions of years old. PRESENTER: All the water on Earth today, every drop, is all the water there has ever been on the planet. But you can get a refresher from the following short video: You must be familiar with the water cycle concept from your early science classes. The amount of water on earth is finite, and the natural water cycle is a system that controls the circulation and redistribution of that resource. To plan sustainable utilization of water resources, we must understand how the water cycle works at the global and local scales. Those industries are important parts of modern infrastructure hence, the water demand must be met to keep the power and food production at the necessary level.
Mining industry utilizes significant amount of water in hydraulic fracturing and oil recovery. It is used as solvent and raw material in chemical manufacturing. For example, water is used as heat transport fluid in thermoelectric energy systems, such as nuclear and fossil fuel fired power plants and concentrating solar power farms. 90% of the earth's fresh water resources is contained in groundwater and ice, and only 10% is water is contained in surface reservoirs - rivers, lakes, wetlands, and streams.Īlthough sustaining life is one of the main key purposes of the water, present-day agriculture and many industry branches heavily rely on the abundance of the water resource. However, only 3% of this reserve is fresh water that can be used for human consumption. More than 70% of the earth surface is covered by water. It is a universal medium that is crucial for sustainability of both ecological and human societies. Water is often envisioned as bloodstream of biosphere. Credit: South Florida Water Management District (via Flickr)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
